
DISTINGUISH BETWEEN PAIR
DISTINGUISH BETWEEN PAIR
Distinguish between the following pairs of compounds :
1. Propanal and Propanone :
Boil both compounds separately with iodine and aqueous sodium carbonate solution. The compound which gives a yellow precipitate is propanone while the other which fails to react is propanal.
CH3COCH3 + 3I2 + 2Na2CO3 →
Propanone
CHI3 + CH3COONa + 2CO2 + H2O
.Yellow ppt. Sodium acetate
.(Iodoform)
.H3CH2CHO + I2 + Na2CO3 → No reaction Propanal
2. Phenol and Benzoic acid :
Phenol and benzoic acid can be distinguished from each other by sodium bicarbonate test. To the solutions of both benzoic acid and phenol, add a smell amount of solid bicarbonate. Whereas benzoic acid gives brisk effervesecence of carbon doxide which turns lime water milky, phenol does not react.
C6OH5COOH + NaHCO3 → C6H5COONa + CO2 + HO2↑ + HI2
3. Pentan-2-one and pentan-3-one :
Both are ketones but pentan-2-one is a methyl ketone whereas pentan-3-one is not. Therefore, they can be distinguished with the help of lodoform test which is given by pentan-2-one and not by pentan-3-one.
CH3COCH2CH2CH3 + 3I2 + 2Na2CO3 ![]() Pentan-2-one
Pentan-2-one
CHI3 + CH3CH2CH2COONa + 3Nal + 2CO2 + H2O
Iodoform Sodium
(yellow ppt.) butanoate
CH 3 CH 2 CO.CH2CH3 + CH3 + I2 + Na2CO3![]()
Pentane-3-01l
4. Ethanal and Propanal:
Ethanal gives yellow ppt. of iodoform when heated with iodine and NaOH.
CH3CHO ![]() CHI3 + HCOONa
CHI3 + HCOONa
. Iodoform
Propanal does not give iodoform test.
5. Acetophenone and Benzophenone :
Acetophenone and benzophenone can be distinguished by iodoform test. Acetophenone, on treatment with I2 and NaOH gives yellow ppt. of iodoform while benzophenone does not give this test.
C6H5COCH3 + 3NaIO → C6H5COONa + CHI3 + 2NaOH
. Sodium Iodoform
. benzoate (yellow ppt.)
6. Benzoic acid and Ethyl benzoate :
(a) Benzoic acid produces effervescence with NaHCO3 solution while ethyl benzoate does not.
(b) Benzoic acid produces vapours of benzene when heated with soda lime (CaO + NaOH) while ethyl benzoate does not.
7. Benzaldehyde and Acetophenone :
Acetophenone, on treatment with I2 and NaOH gives yellow ppt. of iodoform while benzaldehyde does not give this test.
C6H5COCH3 + 3NaIO → C6H5COONa + CHI3 + 2NaOH
. Iodoform
. (yellow ppt.)
8. Ethanol and Acetaldehyde :
Acetaldehyde gives silver mirror test with tollens reagent (Ammonical silver nitrate solution) ethanol does not give this test.
Acetaldehyde reduces Fehling solution and gives red precipitate of Cu2O but ethanol does not give this test.
9. Phenol and carboxylic acid :
Carboxylic acid chemical reacts with sodium bicarbonate and gives effervescence of CO2 phenol does not give this test.
R-![]() -OH + NaHCO3 →R-
-OH + NaHCO3 →R- ![]() -Ō
-Ō ![]() +H2O + CO2 (g) ↑
+H2O + CO2 (g) ↑
With FeCl3 phenol gives violet colour complex.
10. Aldehyde and ketone :
Aldehyde gives the silver mirror test with Tollens reagent and Pred precipitate of Cu2O with Ammonical copper sulphate solution.
R- ![]() – H + 2[Ag(NH3)2]OH →R-
– H + 2[Ag(NH3)2]OH →R- ![]() – OH + 2Ag(s)↓ + 4NH3 + 2H2C
– OH + 2Ag(s)↓ + 4NH3 + 2H2C
.R- ![]() – H+ 2CuO → R-
– H+ 2CuO → R- ![]() – OH + Cu2O↓
– OH + Cu2O↓
Red ppt. of cupreous oxide
Phenol does not give this test.
11. Formic acid and acetic acid :
Formic acid (H – ![]() – OH) has reducing character and reducer Tollens reagent to give silver mirror, reduces Fehling solution to give red ppt. of Cu2O and reduces mercuric chloride to mercureous chloride but acetic acid does not give thin test.
– OH) has reducing character and reducer Tollens reagent to give silver mirror, reduces Fehling solution to give red ppt. of Cu2O and reduces mercuric chloride to mercureous chloride but acetic acid does not give thin test.
12. Primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols :
Test with Lucas reagent (Conc. HCl + anhydreous ZnCl2). Tertiary Alcohol ro 3° Alcohol becomes immediately turbid on reaction with lucas reagent, secondary alcohol after 5 minute and primary alcohol becomes turbid at last.
13. Methylamine and diethylamine :
Heat both these amines with chloroform and alcohol KOH solution. The compound which gives unpleasant (offensive) smell is methylamine while the compound which does not give any smell is diethylamine.
CH3NH2 + CHCl3 + 3KOH ![]() CH3N
CH3N ![]() C+3KCl + 3H2O
C+3KCl + 3H2O
. Methyl
. isocyanide
. (offensive smell)
(CH3)2NH+CHCl3 + 3KOH ![]() No smell
No smell
Dimethylamine
14. Secondary and tertiary amines :
Shake the given amines separately with Hinsberg’s reagent (benzene sulphonyl chloride) in the presence of excess of aqueous KOH solution.
A secondary amine forms N, N-dialky benzene sulphon- amide which remains insoluble in aqueous KOH and even after acidification with dilute HCl.
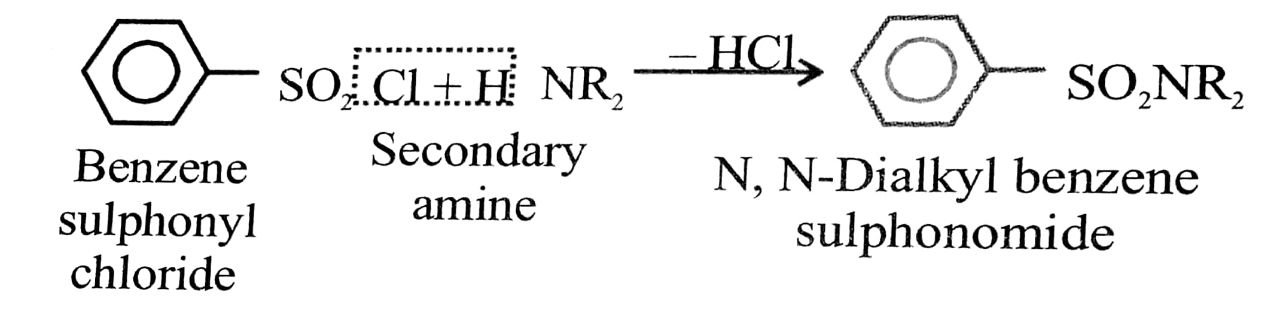
A tertiary amine does not react with benzene sulponyls chloride and remains insoluble in aqueous KOH.

15. Ethylamine and aniline :
To the ice cold solution of both these compounds prepared in excess of dilute HCl, add ice cold solution of sodium nitritet in water and of β—Napthol (2-Naphthol) prepared in dilute in sodium hydroxide solution.
Further cool the reaction mixture in both the cases. The mixture which forms a brilliant orange dye (azodye) contains aniline which the one in which no dye is formed has ehtylamine present in it.

16. Aniline and benzylamine :
Add NaNO2 and HCl to each separately. Cool it to 0 5°C. Then add alkaline solution of phenol. Orange azo dye is formed in alinine. Benzylamine (C6H5CH2NH2) does not form azo dye.
17. Aniline and N-Methylaniline :
Heat both the compounds separately with chloroform and alcoholic KOH. The compound which gives an
unpleasant or offensive smell in aniline while the compounds which does not give any smell is N Methylaniline.
C6H5NH2 + CHCl3 + 3KOI![]() C6H5
C6H5 ![]() C + KCl + 3H2O
C + KCl + 3H2O
Aniline (alc) phenyl isocyanide
. (offensive smell)
C6H5NHCH2 +CHCl3 + 3KOH ![]() Nosmell.
Nosmell.
.N-methyl (alc)
anilin
18. Hinsberg to primary (1° Amine), secondary (2° Amine) and Tertiary (3° Amine) :
Primary Amine on reaction with Hinsberg Reagent benzene sulphonyl chloride (C6H5SO2Cl) will give N-Alkyl benzene sulphonamide which is soluble in NaOH or KOH due to acidic hydrogen.
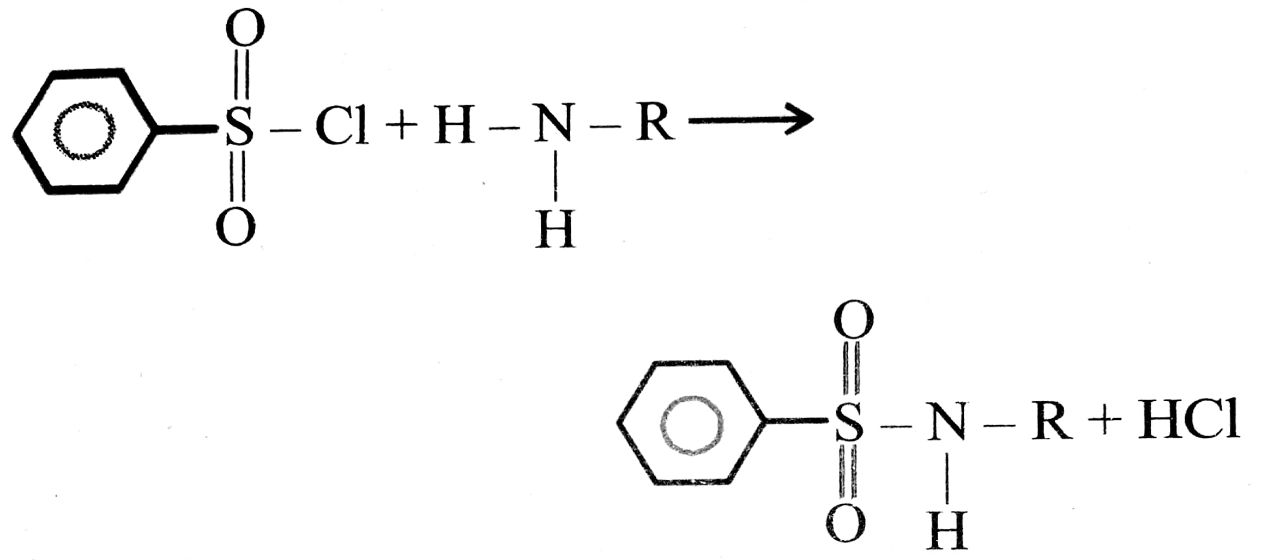
. N-Alkyl benzene Sulphonamide
 Secondary Amine (2° Amine) on chemical reaction with benzene sulphonyl chloride (C6H5 SO2Cl) gives N, N Dialkyl benzene sulphonamide which is not soluble in Alkali NaOH/KOH.
Secondary Amine (2° Amine) on chemical reaction with benzene sulphonyl chloride (C6H5 SO2Cl) gives N, N Dialkyl benzene sulphonamide which is not soluble in Alkali NaOH/KOH.
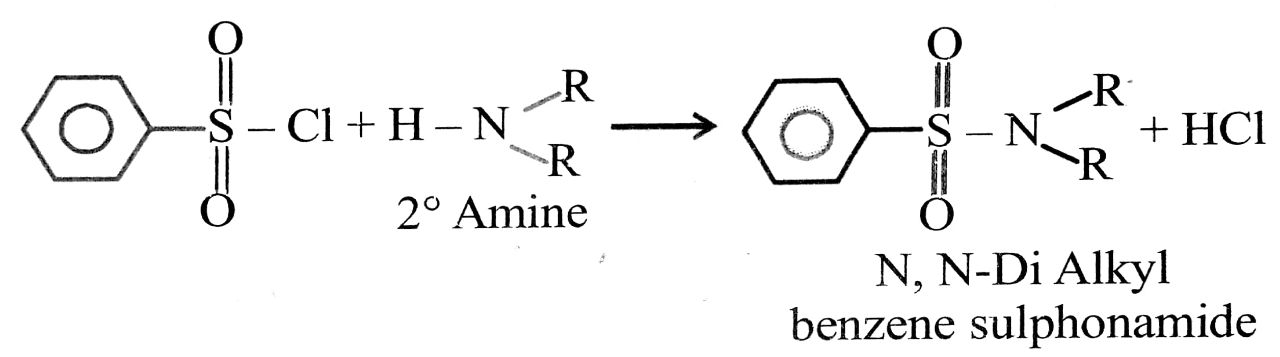
Tertiary Amine (3° Amine) : Tertiary Amine or 3° Amine does not chemically with Hinsberg reagent or benzene sulphonyl chloride.

19. 1°, 2° and 3° alcohols by oxidation method :
On oxidation of 1°, 2° and 3° alcohols are distinguished as below:
1° alcohols on oxidation with K2Cr2O7 and conc. H2SO4 first give aldehyde and then an acid both having same number of carbon atoms as the alcohol have.
K2Cr2O7 + 4H2SO4 → K2SO4 + Cr2(SO4)3 + 4H2O + 3[O]
CH3CH2OH ![]() CH3CHO
CH3CHO ![]() CH3COOH
CH3COOH
2C 2C 2C
2° alcohols on oxidation first gives ketone having same number of C-atoms and then with acid having less number of C-atom.
3° alcohols on oxidation gives ketone and then acid both having less number of C-atoms.

20. Cyclohexane and Cyclohexene
Cyclohexane is an alkene. Its molecule contains a double bond. so, cyclohexene decolourises bromine water. Cycloxexane does not decolourise bromine water.

21. Ethyl chloride (C2H5Cl) and Vinyl chloride (CH2 = CHCl)
Ethyl chloride with AgNO3 gives white precipitate of AgCl. Vinyl chloride does not give this test.
CH3CH2Cl + AgNO3 – White precipitate of AgCl
CH2 = CHCl + AgNO3 – No precipitate
22. Chloroform and dichloromethane
Chloroform (CHCl3) when heated with a primary amine and KOH (alc.) gives an offensive smelling isocyanide (carbylamine) compound, while dichloromethane does not give such reaction.
CHCl3 + RNH2 + 3KOH ![]() RNC + 3KCl + 3H2O chloroform pri. amine
RNC + 3KCl + 3H2O chloroform pri. amine
. carbylamine
. (offensive smell)
23. Chlorobenzene (C6H5Cl) and Benzyl chloride (C6H5CH2Cl)
Chlorobenzene (C6H5Cl) has Cl atom directly bonded to the benzene ring, while in benzyl chloride (C6H5CH2Cl), the Cl atom is in the side-chain. So, benzyl chloride behaves like an aliphatic halide.
When benzyl chloride is reacted with aqueous solution of NaOH, the resulting solution contains NaCl. So, benzyl chloride gives while precipitate with AgNO3 solution in the presence of dil. HNO3.
C6H5CH2Cl![]() C6H5CH2OH + NaCl (aq) benzyl chloride
C6H5CH2OH + NaCl (aq) benzyl chloride
NaCl (aq) + AgNO3 (aq) → AgCl ↓ + NaNO3
. white ppt.
C6H5Cl does not react with NaOH under ordinary conditions. So, chlorbenzene does not give white precipitate with silver nitrate.
24. Bromobenzene (C6H5Br) and Ethyl bromide (C2H5Br)
Bromobenzene has Br atom directly bonded to the benzene ring, while ethyl bromide (bromoethane) is an aliphatic compound. Ethyl bromide when heated with NaOH undergoes substitution reaction.
C2H5Br + NaOH (aq) ![]() C2H5OH + NaBr ethyl bromide
C2H5OH + NaBr ethyl bromide
So, when AgNO3 solution is added to the solution Tobtained above), straw yellow precipitate of silver bromide is formed.
NaBr + AgNO3 → AgBr ↓ + NaNO3
(light yellow ppt.)
Bromobenzene does not give any precipitate on similar treatment.
25. Ethanol (C2H5OH) and Phenol (C6H5OH)
Following tests may be applied to distinguish between ethanol and phenol :
| Test | Ethanol | Phenol | |
| (i) | Litmus test : add 2-3 drops of blue litmus to aqueous solutions of both the compounds. | No change is colour | Blue litmus turns red |
| (ii) | Sodium bicarbonate test : To the aqueous solutions of the compounds add 2-3 drops of saturated sodium bicarbonate solution. | No efferve- scence | Brisk effer- vescence |
| (iii) | Iodoform test : Warm each compound with iodine and NaOH solution separately. | Yellow powder of iodoform | No yellow precipitate |
| (iv) | FeCl3 test : Add 2 drops of neutral FeCl3 to both the compounds separately. | No change in colour | Purple to violet colour (C6H5OH + + Fe3+ → Phenol [Fe(OC6H5]2+ + H+) purple |
26. Phenol (C2H5OH) and Cyclohexanol (C6H11OH)
Phenol is an aromatic compound, while cyclohexanol is an alicyclic compound. The following tests may be performed to distinguish between the two.
| Test | Phenol | Cyclohexanol | |
| (i) | Add 2-3 drops of neutral FeCl3 to each. | Reddish purple- violet colour | No colour |
| (ii) | Add Br2 water and shake | White precipitate of tribromoaphe- nol (C6H5OH + 3Br2 → C6H2Br3. OH + 3HBr) 2, 4, 6- tribromophenol | No change in colour or precipitate |
27. Benzaldehyde (C6H5CHO) and Acetone (CH3COCH3)
Test 1. Acetone gives iodoform test, while benzaldehyde does not.
Reaction : CH3CO.CH2 + 3I2 + 4NaOH → acetone
CHI3 + CH3COONa + 3NaI + 3H2O
iodoform
C6H5CHO ![]() Negative
Negative
benzaldehyde
Test 2. Benzaldehyde reduces Tollens reagent to metallic silver, while acetone does not.
Reaction :
C6H5CHO + 2[Ag(NH3)2]+ + 3OH– ![]() benzaldehyde from Tollen’s reagent
benzaldehyde from Tollen’s reagent
C6H5COO– + 2H2O + 4NH3 + 2Ag
silver mirror
CH3COCH3![]() No silver mirror
No silver mirror
28. Formic acid (HCOOH) and Acetic acid (CH3COOH)
Test 1. Formic acid is a strong reducing agent. It reduces Tollen’s reagent to metallic silver (silver mirror test). Acetic acid does not reduce Tollen’s reagent.
HCOOH + 2[Ag(NH3)2]+ 20H– ![]() 2H2O + CO2 Formic acid from Tollen’s reagent
2H2O + CO2 Formic acid from Tollen’s reagent
+ 2Ag + 4NH3
silver mirror
Test 2. Formic acid reduces Fehling’s solution to red Cu2O, while acetic acid does not.
HCOOH + 2Cu2+ + 40H– → Cu2O + CO2 + 3H2O
Formic acid from Fehling’s solution red ppt.
29. Urea (NH2CONH2) and Acetamide (CH3CONH2)
Both urea and acetamide are solids. Both on heating give off ammonia gas (smell of ammonia). Urea gives biuret test, while acetamide does not.
Bluret test : Heat a small quantity of urea in a dry test tube. Dissolve the residue in small quantity of NaOH solution, and add 1 drop of CuSO4 solution. Appearance of violet colour confirms urea.



