
14. BIOMOLECULES Objective
14. BIOMOLECULES
1. On oxidation with a mild oxidising agent like Br2/H2O, the glucose is oxidized to
(A) saccharic acid
(B) glucaric acid
(C) gluconic acid
(D) valeric acid
2. Invert sugar is
(A) a type of cane sugar
(B) optically inactive form of sugar
(C) mixture of glucose and galactose
(D) mixture of glucose and fructose in equimolar quantities
3. Which of the following compounds is found abundatly in nature ?
(A) Fructose
(B) Starch
(C) Glucose
(D) Cellulose
4. Starch is composed of two polysaccharides which are
(A) amylopectin and glycogen
(B) amylose and glycogen
(C) amylose (20%) and amylopectin (80%)
(D) cellulose and glycogen
5. Maltose is made up of
(A) two α-D-glucose
(B) normal β-D-glucose
(C) α- and β-D-glucose
(D) fructose
6. What is the basic formulae for starch ?
(A) (C6H12O6)n
(B) (C6H10O5)n
(C) C12O22O11
(D) (C6H12O4)n
7. Which of the following is an example of an ldopentose ?
(A) D-Ribose
(B) Glyceraldehyde
(C) Fructose
(D) Erythrose
8. Which of the following treatment will convert starch directly into glucose ?
(A) Heating with dilute H2SO4
(B) Fermentation by diastase
(C) Fermentation by zymase
(D) Heating with dilute NaOH
9. The general formula of carbohydrates is
(A) CnH2n + 1O
(B) CnH2nO
(C) CX(H2O)y
(D) Cn(H2O)2n
10. What are the hydrolysis products of sucrose ?
(A) Fructose + Fructose
(B) Glucose + Glucose
(C) Glucose + Galactose
(D) D-Glucose + D-Fructose
11. The conversion of maltose into glucose is possible by the enzyme
(A) zymase
(B) lactase
(C) maltase
(D) diastase
12. Vhich of the following is a non-reducing sugar ?
(A) Glucose
(B) Sucrose
(C) Maltose
(D) Lactose
13. Which one of the following is not correct ?
(A) D (-) Fructose exist sin faranose structure
(B) D (+) Glucose exists in pyranose structure
(C) In sucrose the two monosaccharides are held together by peptide linkage
(D) Maltose is a reducing sugar
14. Glucose ![]() Product is
Product is
(A) hexanoic acid
(B) gluconi acid
(C) saccharic acid
(D) bromohexane
15. Cellulose ify Saccharide
(A) hexapoly saccharide
(B) pentapolysaccharide
(C) tripolysaccharide
(D) None of these
16. Amino acids generally exist in the form of Zwitter ions. This means they contain
(A) Basic – NH2 group and acidic – COOH group
(B) The basic – NH3 group and acidic-COO-group
(C) Basic – NH2 and acidic – H+ group
(D) Basic – COO- group and acidic – NH3 group
17. Which one of the amino acids can be synthe- sised in the body ?
(A) Alanine
(B) Lysine
(c) Valine
(D) Histidine
18. Denaturation of protein leads to loss of its biological activity by
(A) formation of amino acids
(B) loss of primary structure
(C) loss of both primary and secondary structure
(D) loss of both secondary and tertiary structures
19. Which of the following is an acidic amino acid ?
(A) Glycine
(B) Valine
(C) Leucine
(D) Glutamic acid
20. The melting points of amino acids are higher than the corresponding hal-acids because
(A) amino acids exist as zwitter ions resulting in strong dipole-dipole attraction
(B) amino acids are optically active
(C) due to higher molecular mass of – NH2 group molecular mass of amino acids is higher
(D) they interact with water more than halo-acids and have salt like structure
21. On boiling the egg, what structural changes are taking place in the egg white ?
(A) The colour of the egg changes from colourless to white
(B) 2° and 3° structures are destroyed but 1° structure remains intact
(C) 1°, 2° and 3° structures of egg are destroyed
(D) A reversible change takes place which can be reversed by decreasing the temperature
22. Which one of the following sets of monosaccharides forms sucrose ?
(A) α-D-galactopyranose and α-D-glucopyranose
(B) α-D-glucopyranose and β-D-fructofuranose
(C) β-D-glucopyranose and α-D-fructofuranose
(D) α-D-glucopyranose and β-D-fructopyranose
23. The number of amino acids found in proteins tkaza human body qBP synthesise is
(A) 20
(B) 25
(C) 10
(D) 100
24. Vitamin A is present in
(A) fish liver oil
(B) milk
(C) butter
(D) all of these
25. Which of the following vitamins is water
(A) Vitamin E
(B) Vitamin D
(C) Riboflavin
(D) Retinol
26. Vitamin B2, a water soluble vitamin is also known as
(A) ascorbic acid
(B) riboflavin
(C) thiamine
(D) pyridoxine
27. Which is a fat soluble vitamin ?
(A) Vitamin A
(B) Vitamin B6
(C) Vitamin C
(D) Vitamin B2
28. Vegetable oils like wheat germ oil, sunflower oil, etc. are the good source of
(A) Vitamin K
(B) Vitamin E
(C) Vitamin D
(D) Vitamin A
29. In DNA, the complimentary bases are
(A) uracil and adenine, cytosine and guanine
(B) adenine and thymine, guanine and cytosine
(C) adenine and thymine, guanine and uracil
(D) adenine and guanine, thymine and cytosine
30. RNA is a
(A) single helix strand
(B) double helix strand
(C) right hand twisted double helix strand
(D) triple helix strand
31. The double strand helix structure of DNA was proposed by
(A) Har Gobind Khurana
(B) Watson and Crick
(C) A. R. Todd
(D) G. W. Kenner
32. Which of the following acids is a vitamin ?
(A) Aspartic acid
(B) Ascrobic acid
(C) Adipic acid
(D) Saccharic acid
33. Dinucleotide is obtained by joining two nucleotides together by phosphodiester linkage. Between which carbon atoms of pentose sugars of nucleotides are these linkages present ?
(A) 5′ and 3′
(B) l’ and 5′
(C) 5′ and 5′
(D) 3′ and 3′
34. Which of the following B-group vitamins can be stored in our body ?
(A) Vitamin B1
(B) Vitamin B2
(C) Vitamin B6
(D) Vitamin B12
35. Which of the following bases is not present in DNA ?
(A) Adenine
(B) Thymine
(C) Cytosine
(D) Uracil
36. Three cyclic structures of monosaccharides are given below. Which of these are anomers ?
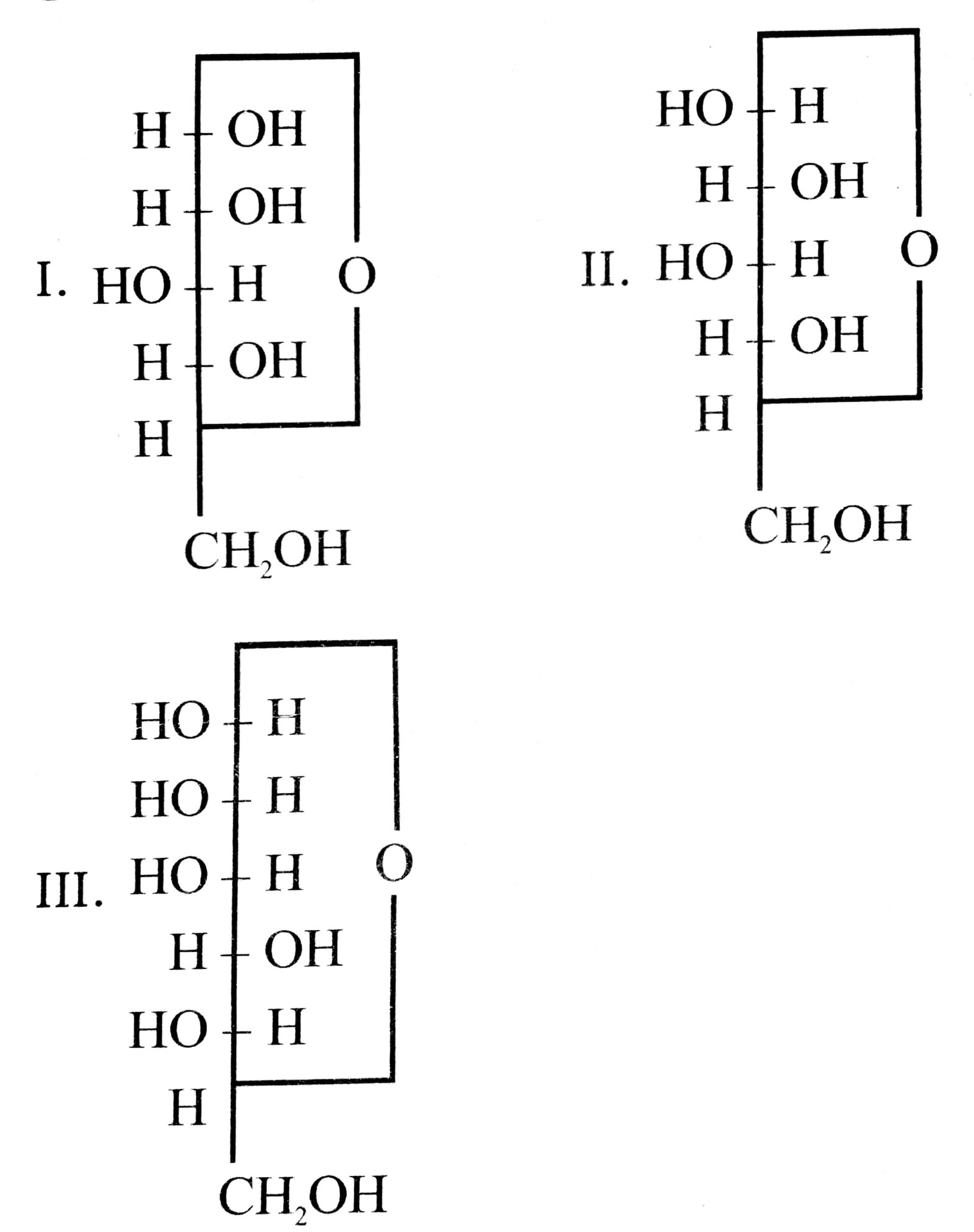
(A) I and II
(B) II and III
(C) I and III
(D) III is anomer of I and II



