
12. ALDEHYDES, KETONES AND CARBOXYLIC ACIDS Objective
12. ALDEHYDES, KETONES AND CARBOXYLIC ACIDS
1. Propanone can be prepared from ethyne by
(A) passing a mixture of ethyne and steam over a catalyst, magnesium at 420°C
(B) passing a mixture of ethyne and ethanol over a catalyst zinc chromite
(C) boiling ethyne with water in the presence of HgSO4 and H2SO4
(D) treating ethyne with iodine and NaOH
2. The addition of HCN to carbonyl compounds is an example of
(A) nucleophilic addition
(B) electrophilic addition
(C) free radical addition
(D) electromeric addition
3. Aldehydes other than formaldehyde react with Grignard’s reagent to give addition products which on hydrolysis give
(A) tertiary alcohols
(B) secondary alcohols
(C) primary alcohols
(D) carboxylic acids
4. Which of the following will not give aldol condensation ?
(A) Phenyl acetaldehyde
(B) 2-Methylpentanal
(C) Benzaldehyde
(D) 1-Phenylpropanone
5. Identify reactant (X) in the given reaction sequence
CH3COCH3 + x → (CH3)3C – OMG – Cl ![]() (CH3)3C – OH +
(CH3)3C – OH + ![]()
(A) CH3MgCl
(B) CH3COCl + Mg
(C) MgCl2
(D) CH3CH2MgCl
6. α-Hydroxypropanoic acid can be preapred from ethanal by following the steps given in the sequence
(A) Treat with HCN followed by acidic hydrolysis
(B) Treat with NaHSO3 followed by reaction with Na2CO3
(C) Treat with H2SO4 followed by hydrolysis
(D) Treat with K2Cr2O7 in presence of sulphuric acid
7. What is the testto differentiate between penta-2-one and pentan-3-one ?
(A) Iodoform test
(B) Benedict’s test
(C) Fehling’s test
(D) Aldol condensation test
8. Study the given reaction and identify the process which is carried out

(A) It is used for purification of aldehydes and ketones
(B) It is used to distinguish aldehydes from ketones
(C) It is used to prepare cyclic aldehydes and ketones
(D) It is used to study polar nature of aldehydes and ketones
9. Hydrocarbons are formed when aldehydes and ketones are reacted with amalgamated zinc and conc. HCl. The reaction is called
(A) Cannizzaro reaction
(B) Clemmensen reduction
(C) Rosenmund reduction
(D) Wolff-Kishner reduction
10. The order of reactivity of CH3CHO, CH3COC2H5 and CH3COCH3 is
(A) CH3CHO > CH3COCH3 > CH3COC2H5
(B) C2H5COCH3 > CH3COCH3 > CH3CHO
(C) CH3COCH3 > CH3CHO > C2H5COCH3
(D) CH3COCH3 > C2H5COCH3 > CH3CHO
11. Which among the following is most reactive to give nucleophilic addition ?
(A) FCH2CHO
(B) ClCH2CHO
(C) BrCH2CHO
(D) ICH2CHO
12. 
The product (X) will be
. CH2ONa
(A) |
. COONa
. COOH
(B) |
. COOH
. CH2OH
(C) |
. COONa
. CH2OH
(D) |
. CH2OH
13. Find the product of the given reaction
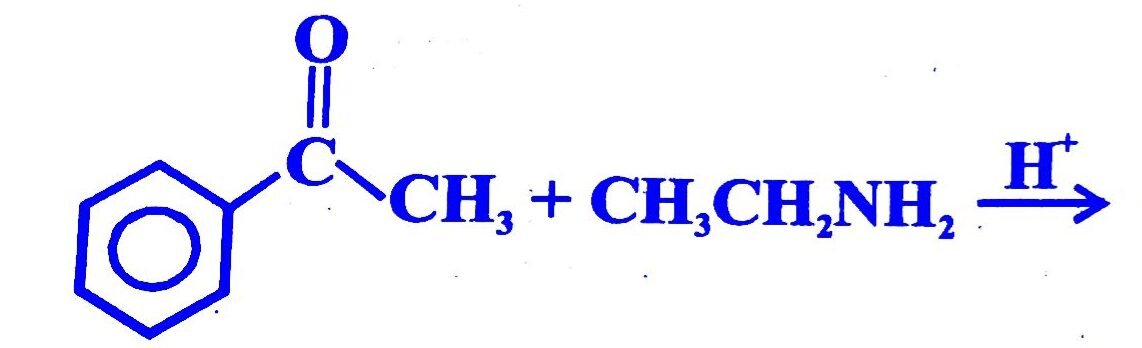
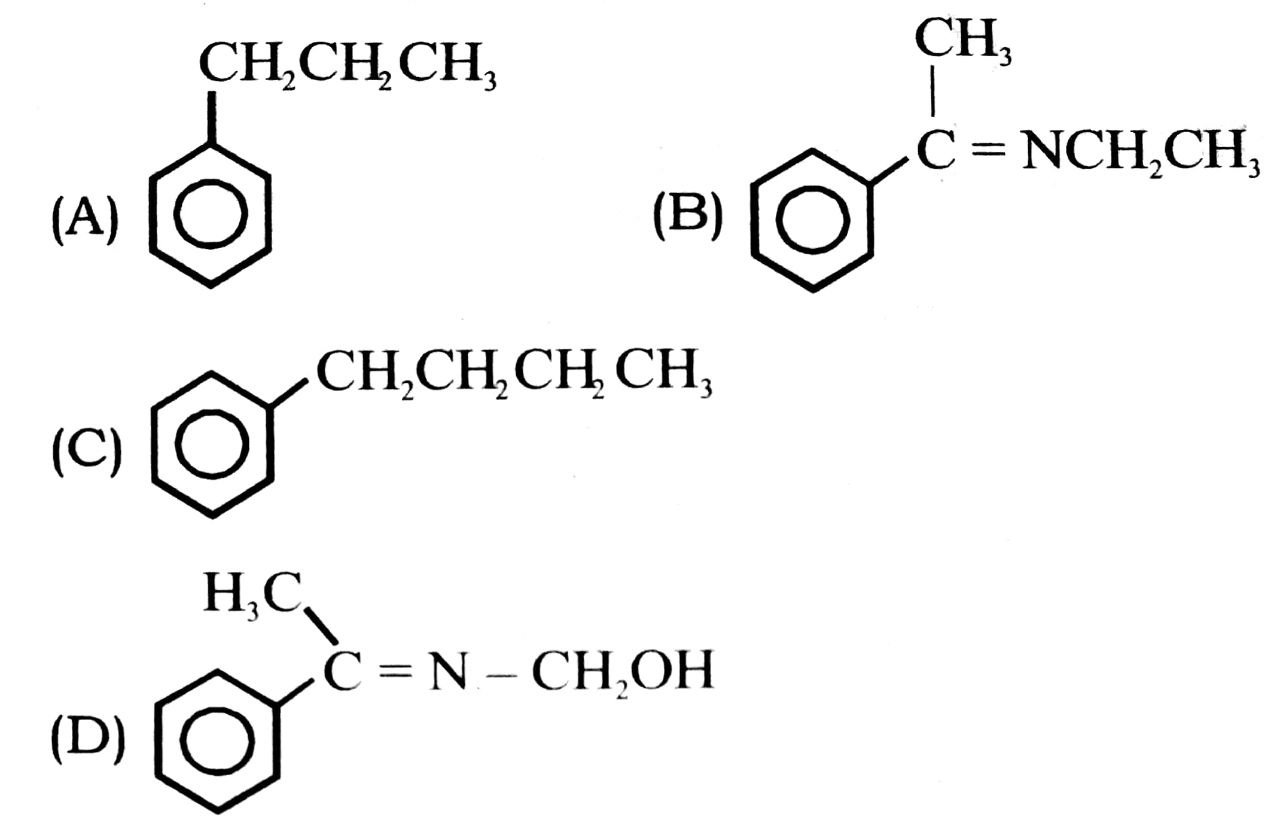
14. When propanal reacts with 2-methylpropanal in presence of NaOH, four different products are formed. The reaction is known as
(A) Aldol condensation
(B) Cross aldol condensation
(C) Cannizzaro reaction
(D) HVZ condensation
15. Which of the following IUPAC names is not correctly matched ?
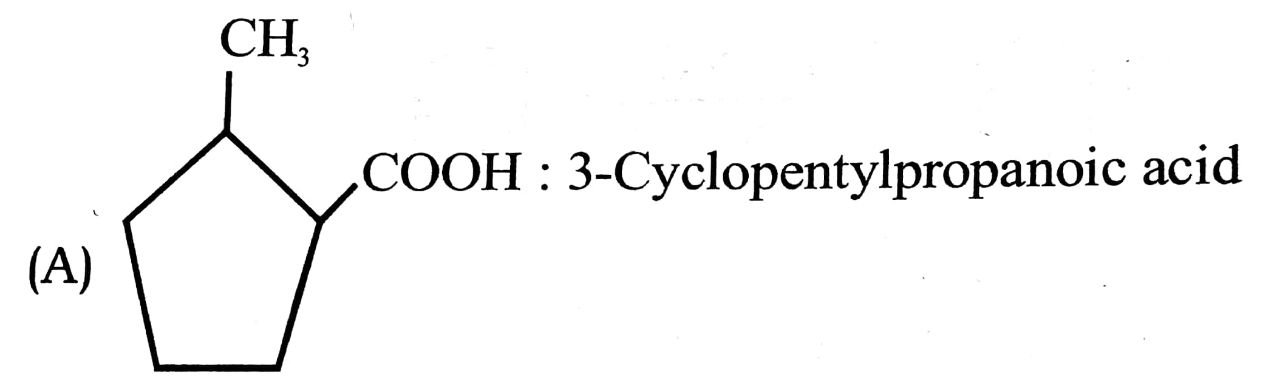
(B) (CH3)2C = CHCOOH : 3-methylbut-2-enoic acid
(C) PhCH2CH2COOH : 3-Phenylpropanoic acid

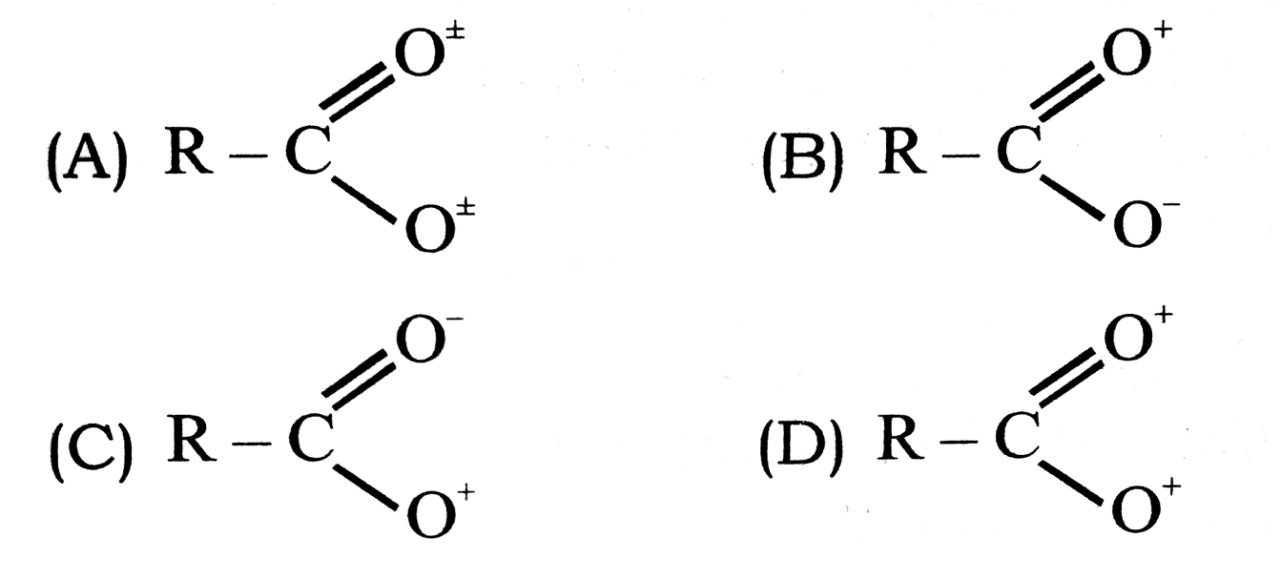
16. The correct structure representation of carboxylate ion is
17. Identify (x) and (Y) in the given reaction sequence
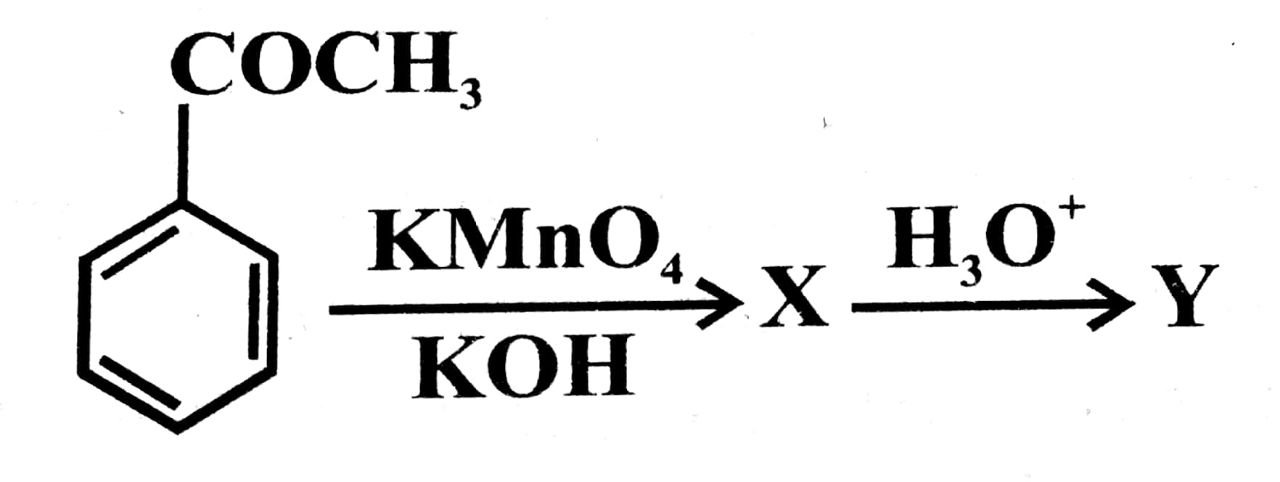


18. Which of the following reactions does not occur ?

19. What are the correct steps to convert acetal-dehyde to acetone ?
(A) CH3MgBr, H2O, Oxidation
(B) Oxidation, Ca(OH)2, Heat
(C) Reduction, KCN, Hydrolysis
(D) Oxidation, C2H5ONa, Heat
20. What happens when a carboxylic acid is treated with lithium aluminium hydride ?
(A) Aldehyde is formed
(B) Primary alcohol is formed
(C) Ketone is formed
(D) Grignard reagent is formed
21. Acetic acid can be halogenated in presence of phosphorous and chlorine. Formic acid cannot be halogenated with same way because of
(A) presence of α-H atom in formic acid
(B) presence of α-H atom in acetic acid
(C) absence of α-H atom in CH3COOH
(D) higher acidic strength of acetic acid than formic acid
22. Which of the following is the correct order of relative strength of acids ?
(A) ClCH2COOH > BrCH2COOH > FCH2COOH
(B) BrCH2COOH > ClCH2COOH > FCH2COOH
(C) FCH2COOH > ClCH2COOH > BrCH2COOH
(D) ClCH2COOH > FCH2COOH > BrCH2COOH
23. The correct order of increasing acidic strength is
(A) phenol < ethanol < chloroacetic acid < acetic acid
(B) ethanol < phenol < chloroacetic acid < acetic acid
(C) ethanol < phenol < acetic acid < chloroacetic acid
(D) chloroacetic acid < acetic acid < phenol < ethanol
24. The reagent which does not react with both, acetone and benzaldehyde is
(A) Sodium hydrogensulphite
(B) Phenyl hydrazine
(C) Fehling’s solution
(D) Grignard reagent
25. CH3 – C ≡ CH ![]() CH3 – C – CH3
CH3 – C – CH3
. ||
. O
Structure of ‘A’ and type of isomerism in the above reaction are respectively
(A) prop-1-en-2-ol, metamerism
(B) prop-1-en-1-ol, tautomerism
(C) prop-2-en-2-ol, geometrical isomerism
(D) prop-1-en-2-ol, tautomerism
26. Which of the following compounds will give butanone on oxidation with alkaline KMnO4 solution ?
(A) Butan-1-ol
(B) Butan-2-ol
(C) Both of these
(D) None of these
27. In Clemmensen reduction carbonyl compound is treated with
(A) Zinc amalgam + HCI
(B) Sodium amalgam + HCI
(C) Zinc amalgam + nitric acid
(D) Sodium amalgam + HNO3
28. Carbon atom in the carbonyl group is
(A) sp-hybridised
(B) sp2-hybridised
(C) sp3-hybridised
(D) dsp2-hybridised
29. The reaction is called
RCOCl + H2 ![]() RCHO + HCl
RCHO + HCl
(A) Cannizzaro reaction
(B) Rosenmund’s reaction
(C) Haloform reaction
(D) Clemensen’s reaction
30. Which of the following undergoes Cannizzaro’s reaction ?
(A) CH3CHO
(B) CH3CH2CHO
(C) (CH3)2CHCHO
(D) HCHO
31. Paraldehyde is a trimer of
(A) Methanol
(B) Ethanol
(C) Butanol
(D) None




