
12. ALDEHYDES. KETONES AND CARBOXYLIC ACIDS – LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
12. ALDEHYDES. KETONES AND CARBOXYLIC ACIDS
Q. 1. Explain the following and give an example:
(i) Cyanohydrin
(ii) Acetal
(iii) Semicarbazone
(iv) Aldol
(v) Hemiacetal
(vil) Oxime
(vii) Ketal
(viii) Amine
(ix) 2, 4-DNP-derivative
(x) Schiff’s base.
Ans⇒ (i) Cyanohydrin : Aldehydes and ketones react with hydrogen cyanide. HCN to form the addition products called cyanohydrins.

(ii) Acetal : It is dialkoxy compound formed by the reaction of aldehyde and two moles of alcohols, e.g.

(iii) Semicarbazone : Aldehydes and ketones react with semicarbazide to form semicarbazones.
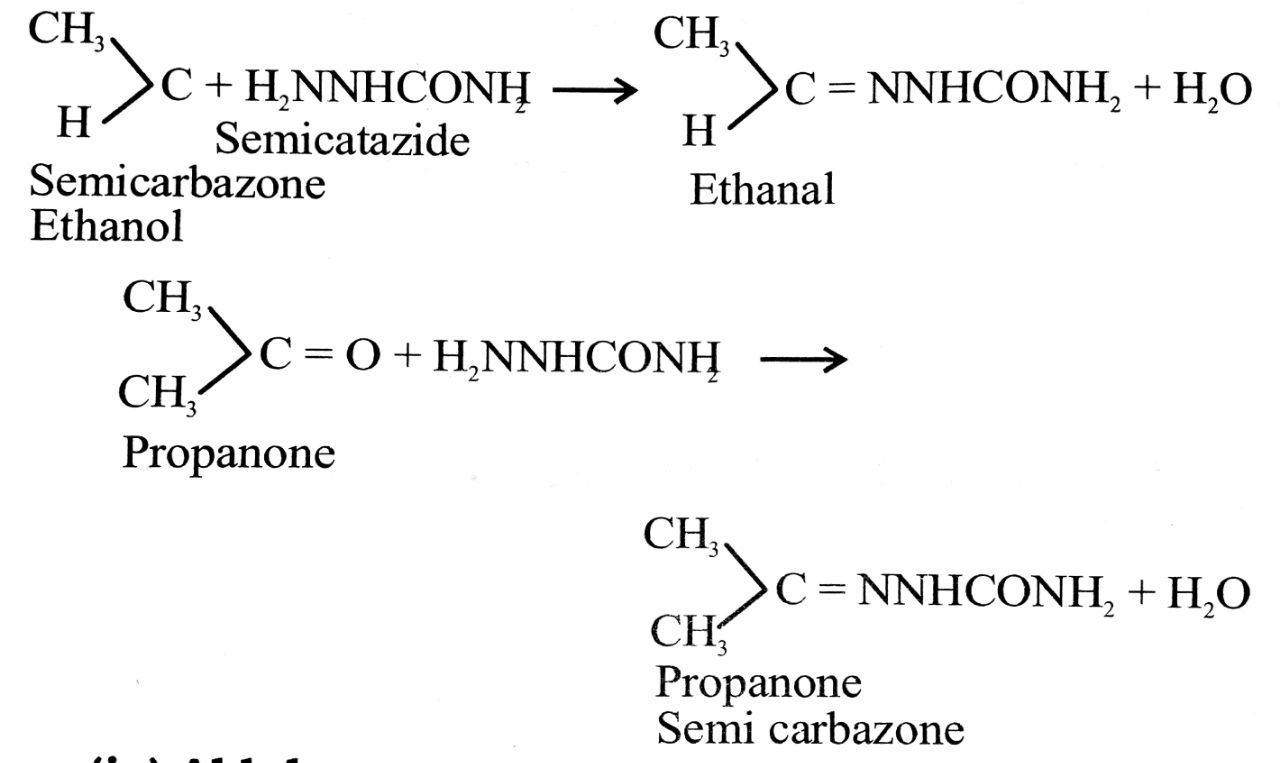
(iv) Aldol : The compounds having alcoholic group and aldehyde or ketone group are called aldols, e.g.,
![]()
(v) Hemi-acetal : It is formed by the reaction of aldehyde with one mole of alcohol. It contains both alcohol and alkoxy group e.g.,

(vi) Oxime : When aldehydes and ketones react with NH2OH (hydroxylamine) oximes are formed.
> C = O + H2N ![]() C= NOH + H2O
C= NOH + H2O
. oxime
(vii) Ketal : Ketones react with dihydroxy compounds to form cyeliketals.

(viii) Amine : It is an organic derivative of ammonia in which one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced with alkyl or aryl groups.
NH3 HR-NH2 R-NH-R R-![]() -R
-R
Ammonia primary Seccondary Tertiary
.amine amine amine amine
(ix) 2, 4-DNP derivative : Its structure is

It is short name 2, 4-Dinitrophenyl hydrazine. 2, 4 DNP derivatives are yellow, orange or red solids, useful for characterisation of aldehydes and ketones.
(x) Schiff’s base : They are the class of compounds having general formula C6H5-N=CR2, where ‘R’ is alkyl or aryl group or hydrogen atoms. It is formed by reaction of primary aromatic amine with aldehydes or ketones. It turns aldehyde pink.
Q. 2. Write equations of the following reactions :
(i) Friedel craft reaction-alkylation of anisole.
(ii) Nitration of anisole.
(iii) Bromination of anisole in ethanoic acid medium.
(iv) Friedel craft’s acetylation of anisole.
Ans⇒
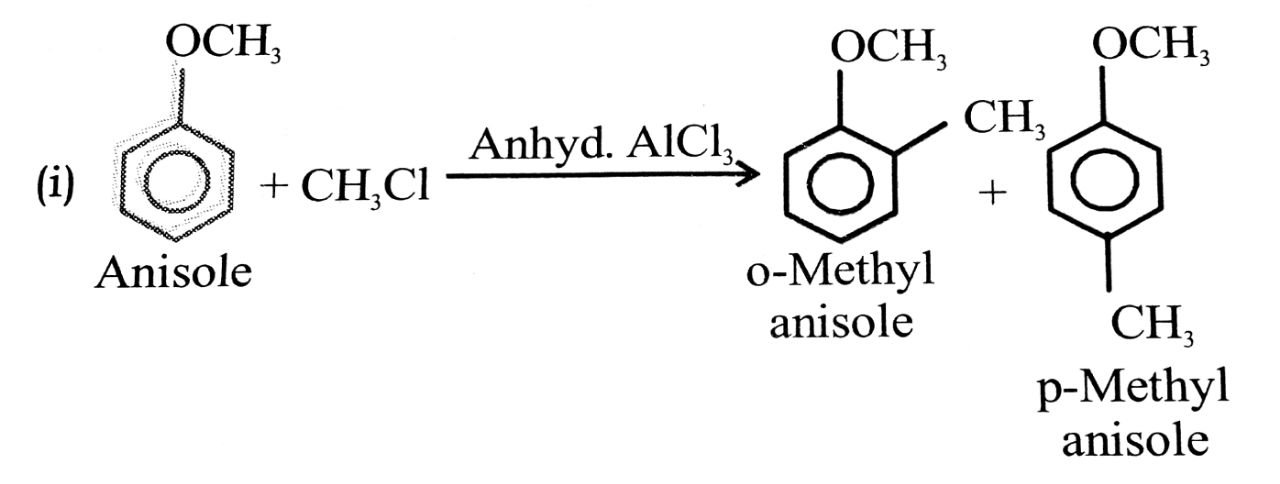
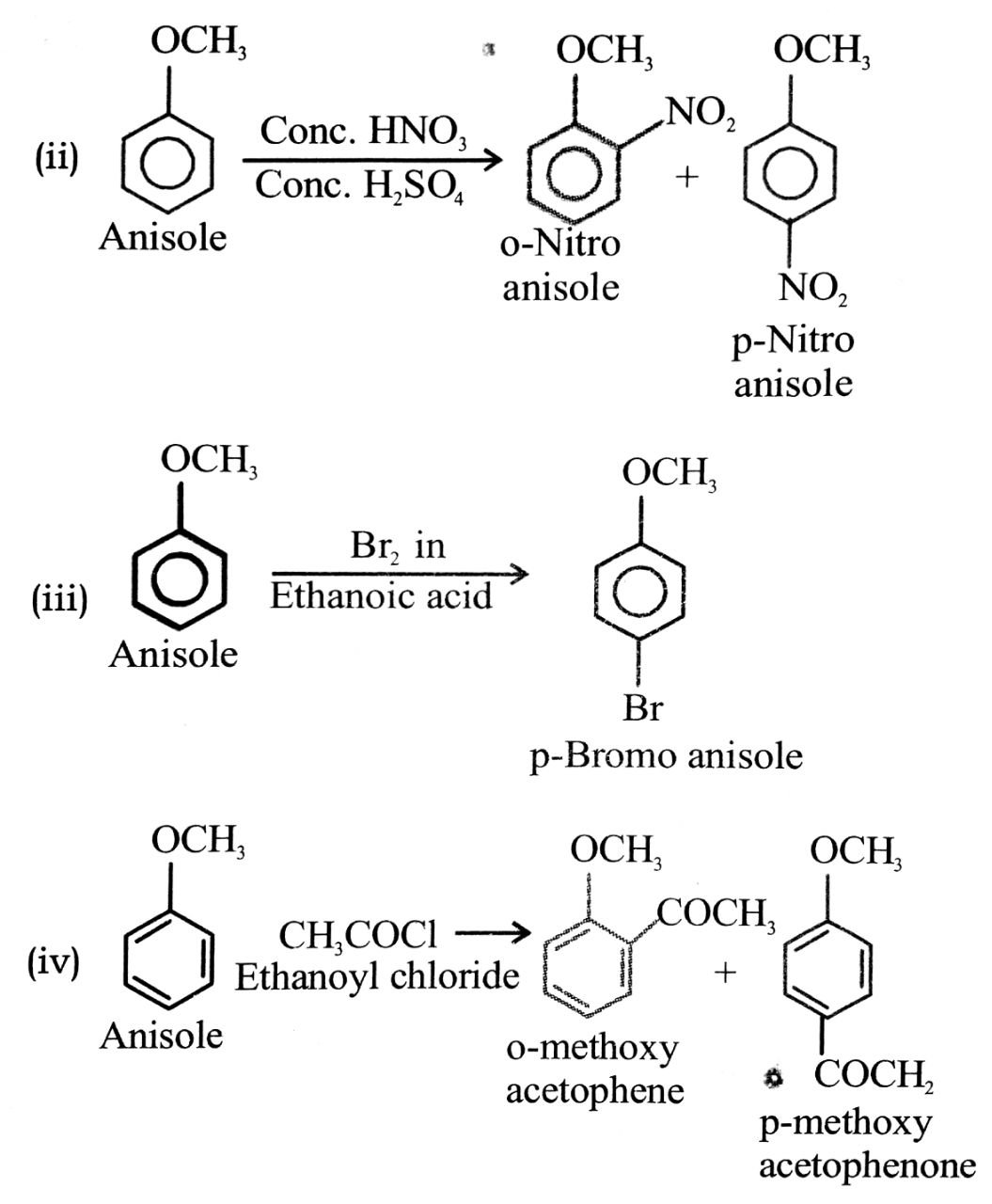
Q. 3. Explain phenol is more acidic than aliphatic alcohol, Why?
Ans⇒ The strength of acid depends on the stability of its conjugate base. When phenol releases Ht and forms phenoxide ion (C6H5O–) which is a conjugate base of phenol which under resonance and stablises it and hence phenol is more acidic.
But in case of Aliphatic alcohol (ROH) it also forms alkoxide ion (RO–) after loosing H+ but it is not stablised due to inability to form resonance.

I, II and III is the resonating structure of phenoxide ion showing resonance.
R-OH ![]() R-O– + H+
R-O– + H+
Alkyl Alcohol Alkoxide
But in case of Aliphatic alcohol it does not shows resonace and the reaction becomes reversible.
Q. 4. What is Lucas test of turbidity of 1° alcohol, 2° alcohol and 3° alcohol ?
Ans⇒ Lucas reagent is anhydrous ZnCl2 + Conc. HCI.
(R3C – OH) 3° Alcohol (Tertiary Alcohol) becomes turbid immediate by the formation of chloride with lucas reagent.
2° Alcohol (Secondary alcohol R2C – H) becomes Turbid after 5 minute by the formation of chloride with lucas reagent.
1° Alcohol (Primary Alcohol) becomes turbid at last by the formatiion of chloride with lucas reagent.
The amount of turbidity formation depends on the stability of carbocation which is as follows :
3° Carbocation > 2° Carbocation > 1° Carbocation R3C+ > R2C+H > R+CH2
Q. 5. How will you obtain aldehydes from primary alcohols ?
Ans⇒ Preparation of aldehydes from primary alcohols :
(i) By the oxidation of alcohols : An aldehyde is prepared when a primary alcohol is oxidised by acidified potassium dichromate under controlled conditions.

(ii) By catalytic dehydrogeneration of alcohol : By passing vapours of a primary alcohol over hot reduced copper at 573 K, we get an aldehyde.

Q. 6. How will you prepare ketones from alcohols ?
Ans⇒ Preparation of ketones from alcohols : Ketones can be prepared from secondary alcohols either ‘ by oxidation or by catalytix dehydrogeneration.
(i) Oxidation of secondary alcohol:
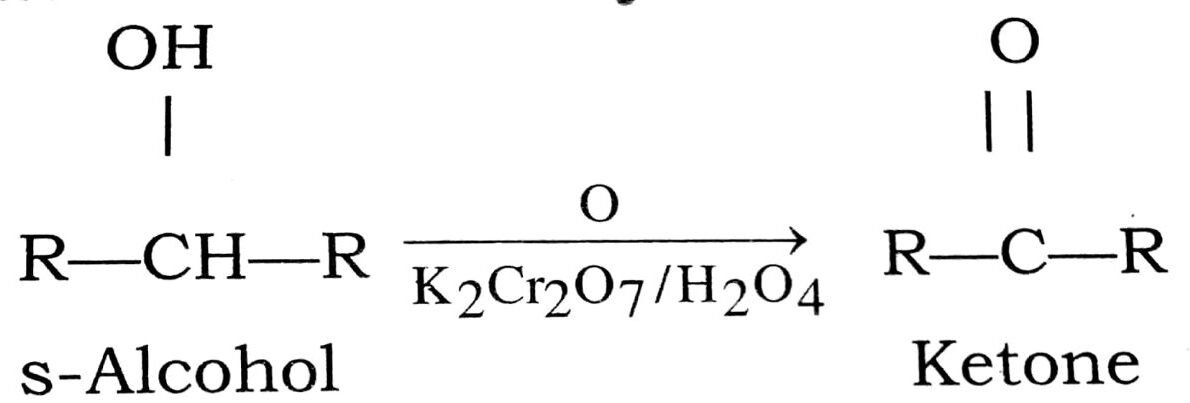
(ii) Catalytic dehydrogeneration of secondary alcohol :

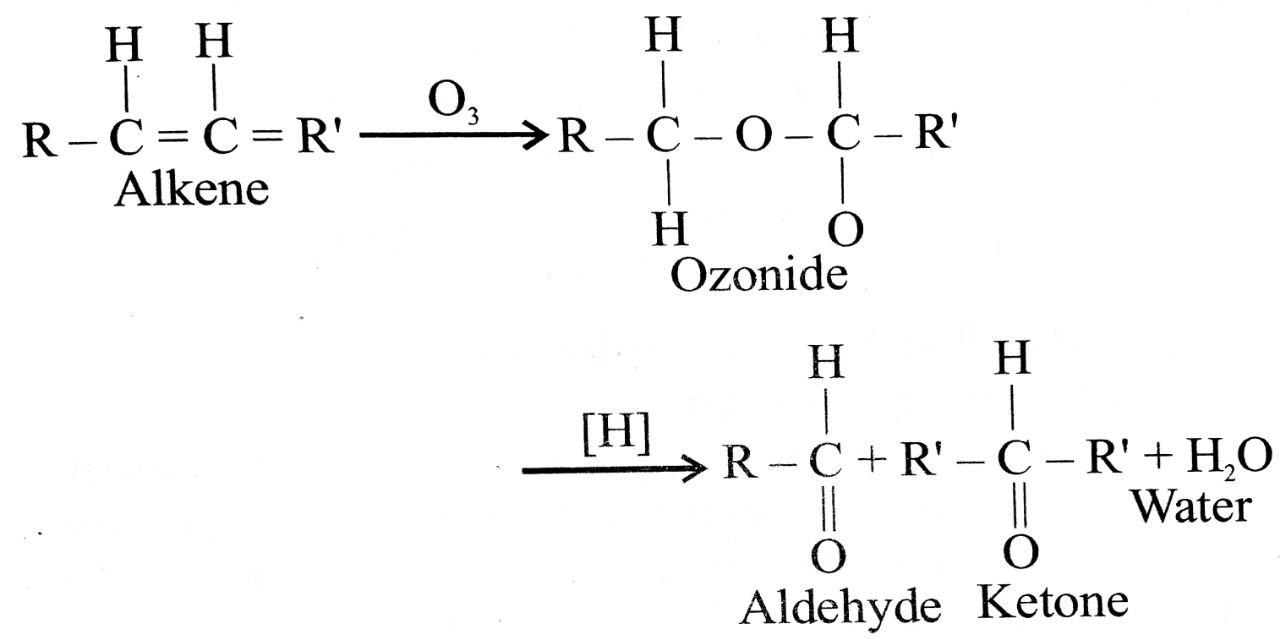
Q. 7. Discuss the preparation of aldehydes and ketones from alkenes.
Ans⇒ (i) By oxidation of alkenes with ozone followed by the redcution of the ozonide by zinc and ethanoic
acid or hydrogen on palladium, aldehydes and ketones are formed.

(ii) If out of the two doubly-bonded carbon atoms in alkene only one carbon contains a hydrogen atom, a mixture of aldehyde and ketone will be obtained.
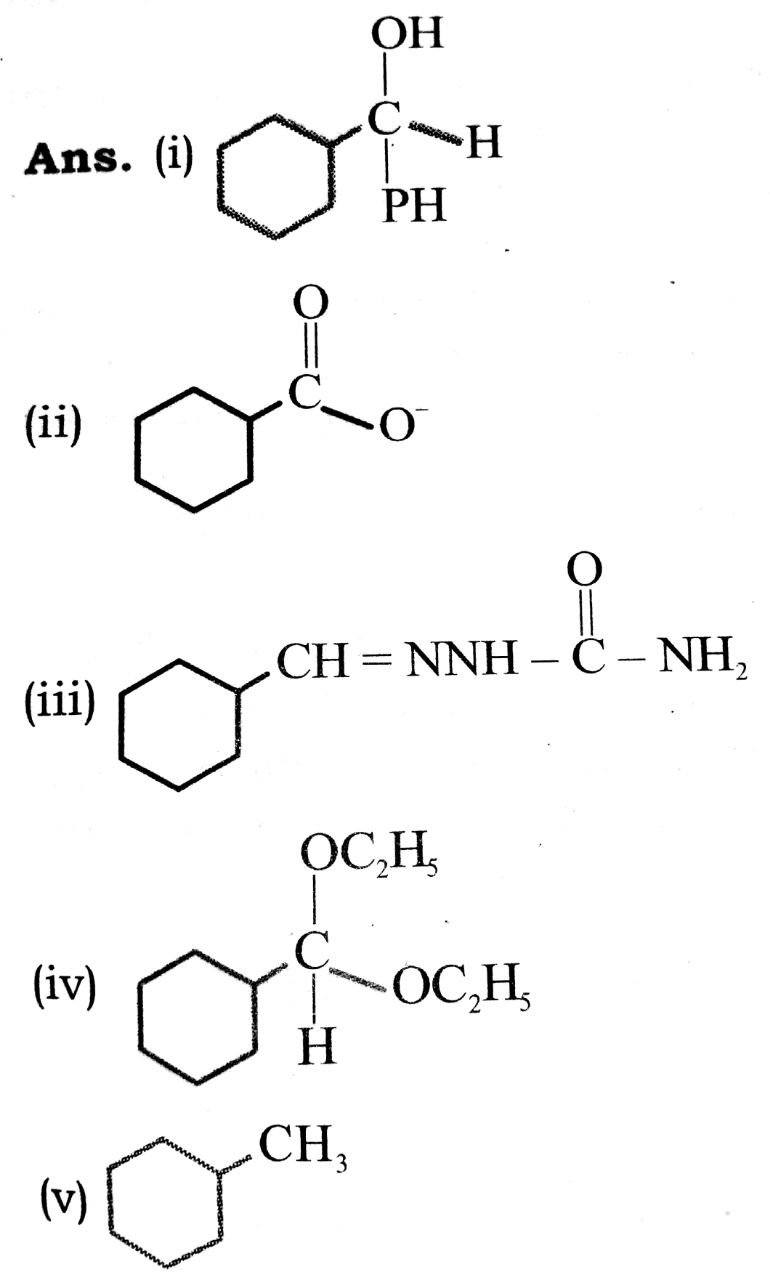
Q. 8. Predict the product formed when cyclohexane carbaldehyde reacts with following agents :
(i) PhMgBr then H3O
(ii) Tollen’s reagent
(iii) Semicarbazide and weak acid
(iv) Excess ethanol and acid
(v) Zinc amalgam and dilut hydrochloric acid.
Q. 9. Describe the following:
(i) Acetylation
(ii) Cannizzaro reaction
(iii) Cross aldol condensation
(iv) Decarboxylation.
Ans⇒ (i) Acetylation : Acetylation is the replacement of H atom of alcohols, amines and other such compounds with acetyl group, e.g.,
C2H5OH + CICOCH 3 → CH 3COOC 2H5 + HCl

(ii) Cannizzaro’s reaction : In this reaction two molecules of aldehydes (without the a-hydrogen atom) react in presence of concentrated alkali by mutual oxidation-reaction forming one molecule of each of the corresponding alcohol and acid. Thus
Methanol when heated with alkali gives methanol and methanoic acid.

(iii) Cross-aldol condensation : Aldol condensation of a mixture of two different aldehydes or/and ketones each containing a α-hydrogen gives a mixture of four products. Two products are made up of two moelcules of same carbonyl compounds and are same as in case of simple aldol condensation. The other two products arise from the reaction between one molecule each of two different carbonyl compounds. These are called cross aldol condensation products and the reaction leading two formation of these products is known as cross-aldol condensation. Example :

(simple aldol condensation products)

(cross aldol condensation products)
(iv) Decarboxylation : Carboxylic acid lose carbon dioxide, when their sodium salts are heated with soda lime (NaOH + Cao). The reaction is known as Decarboxylation.

Q. 10. (a) Write IUPAC name of the compound
![]()
(b) Account for the following:
(i) Aldehydes are more reactive than Ketones towards nucleophilic addition reaction.
(ii) Chloroacetic acid is stronger acid than acetic acid
Ans⇒
(a)![]() 3-oxopentanoic acid
3-oxopentanoic acid
(b) (i) The reactivity of the carbonyl group to wards the nucleophilic addition reaction depends upon the magnitude of positive charge on the carbonyl carbon atom. Introduction of alkyl group (+ I effect) decreases the reactivity ketone has two alkyl groups while the aldehydes have only one. So aldehydes are more reactive towards nucleophilic addition reactions.
(ii) In presence of electron withdrawing group (-I effect) strength of carboxylic acids increases. Hence chloroacetic acid is stronger acid than acetic acid.
Q. 11. Why is benzoic acid a stronger acid than phenol ?
Ans⇒ Benzoic acid is a stronger acid than phenol because the benzoate ion is stabilised by two equivalent reasonance structure in which the negative charge is present at the more electronegative oxygen atom.
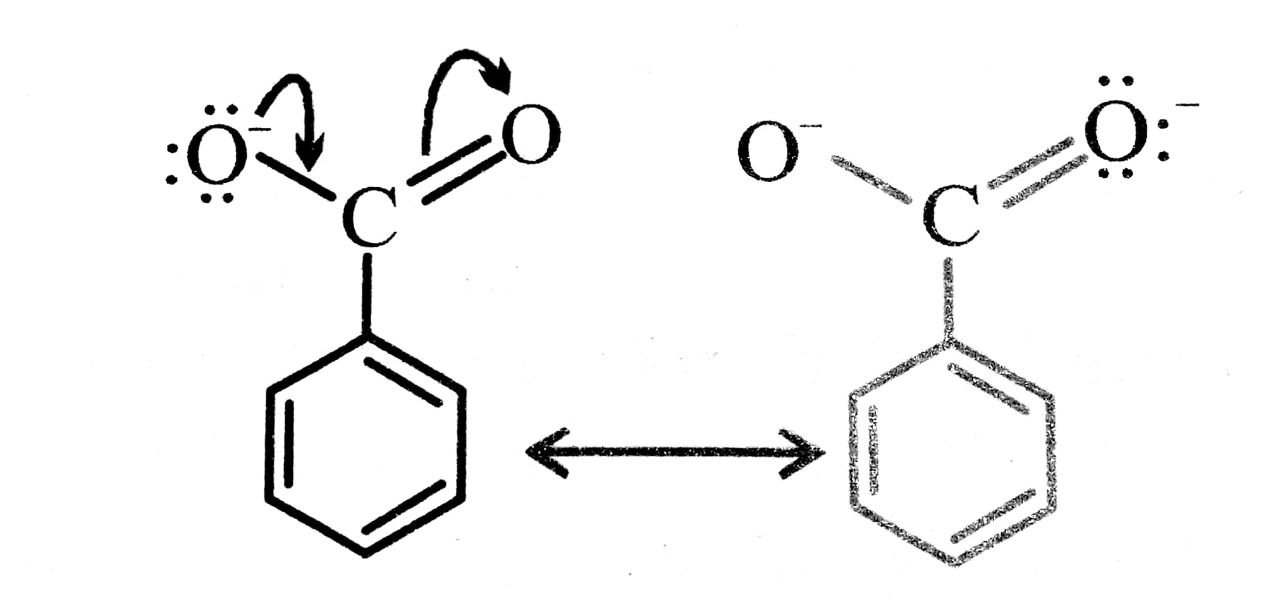
The conjugate base of phenol, a phenoxide ion, has non-equivalent resonance structure in which the negative charge is at the less electronegative carbon atom. Thus, the benzoate ion is more stable than phenoxide ion. Hence benzoic acid is a stronger acid than phenol.

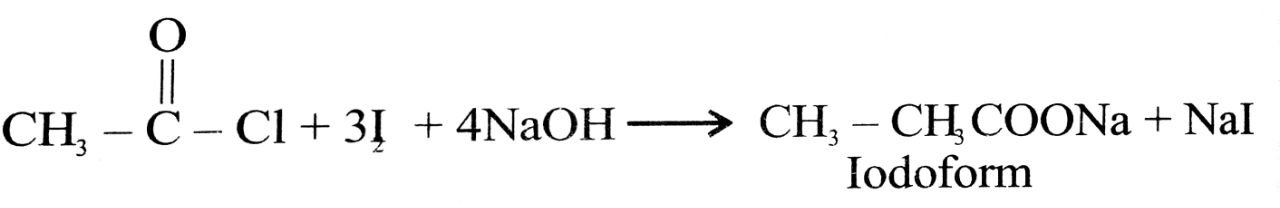
Q. 12. (a) What happens when :
(i) Aldehyde is treated with methyl magnesium bromide and then hydrolysed.
(ii) Acetyl chloride is heated with hydrogen in presence of boiling Xylene Pd-supported by BaSO4
(iii) Propanone is treated with I2 and NaOH.
(d) Identify the products A and B in the following reactions.
(i) CH3CHBr![]() [A]
[A]![]() [B]
[B]
(ii) (CH3COO)2Ca ![]() [A]
[A]![]() [B]
[B]
Ans⇒ (a) (i) Isopropyle alcohol (2०) is obtained

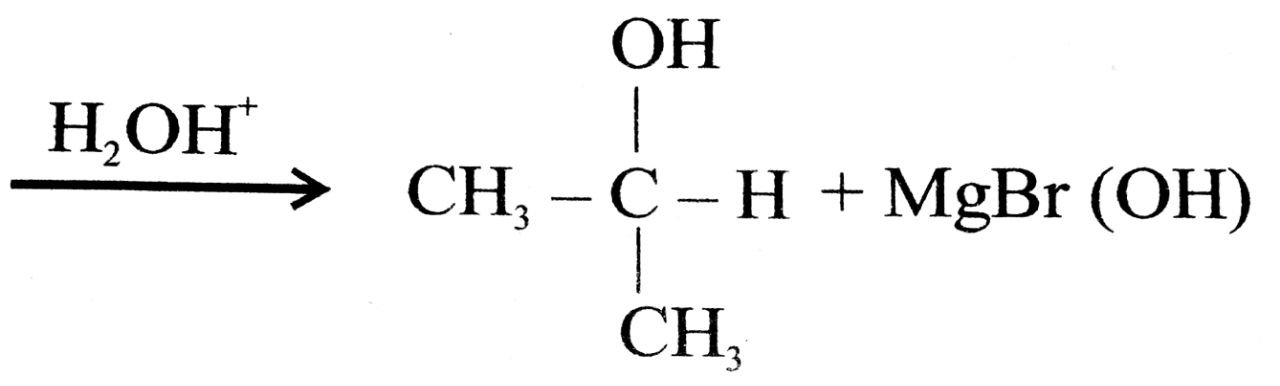
(ii) Acetal dehyde is obtained

(iii) Iodoform is obtained
(b) (i) A = CH3CH3OH Ethyl alcohol
B = CH3COOH Acetic acid
(ii) A = CH3COH3Acetone
B = CH3CH2CH3 Propane



