
10. HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES Objective
10. HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES
1. Good conductor of electricity and heat is
(A) Anthracite coke
(B) Diamond
(C) Graphite
(D) Charcoal
2. In which of the following allotropes of carbon, percentage of carbon is maximum ?
(A) Wood charcoal
(B) Coconut charcoal
(C) Graphite
(D) None of these
3. The hybridisation of carbon in diamond is
(A) sp3
(B) sp2
(c) sp
(D) dsp2
4. Organic compound must contain an element
(A) oxygen
(B) carbon
(C) hydrogen
(D) nitrogen
5. Alkene gives which of the following reactions ?
(A) Addition reaction
(B) Substitution reaction
(C) Both (A) and (B)
(D) None of these
6. Single bond length between carbon-carbon is
(A) 1.34 Å
(B) 1.20 Å
(C) 1.54 Å
(D) none of these
7. Valency of carbon is
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
8. Criteria for purity of organic solid is
(A) boiling point
(B) melting point
(C) specific gravity
(D) none of these
9. General formula of Alkene is
(A) CnH2n
(B) CnH2n + 2
(C) CnH2n – 2
(D) none of these
10. Hybridisation of carbon in ethane is
(A) sp3
(B) sp2
(C) sp
(D) sp3d2
11. Number of π bonds in ethyne is
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
12. The compound having general formula CnH2n + 2 is
(A) Alkene
(B) Alkyne
(C) Alkane
(D) none of these
13. The antiseptic action of CHI3 is
(A) due to idoform
(B) due to liberation of free iodine
(C) partially due to iodine and partially due to CHI3
(D) none of these
14. Which of the following is not correctly matched with its IUPAC name ?
(A) CHF2 CBrCIF : 1-Bromo- 1 -chloro- 1, 2, 2- trifluoroethane
(B) (CCl3)3CCl : 2-(Trichloromethyl)-1, 1, 2, 3, 3- heptachloropropane
(C) CH3C (p-ClC6H4)2 CH(Br)CH3 : 2-Bromo-3, 3-bis (4-chlorophenyl) butane
(D) o-BrC6H4CH (CH3) CH2CH3 : 2-Bromo-1- methylpropylbenzene
15. The reaction
CH2 = CH – CH3 + HBr → ![]() 3– CH-CH3 is an example of
3– CH-CH3 is an example of
(A) nucleophilic addition
(B) free radical addition
(C) electrophilic addition
(D) electrophilic substitution
16. 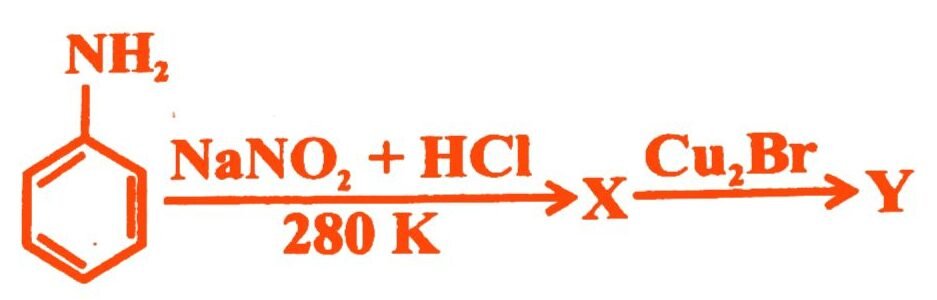
X and Y in the reaction are
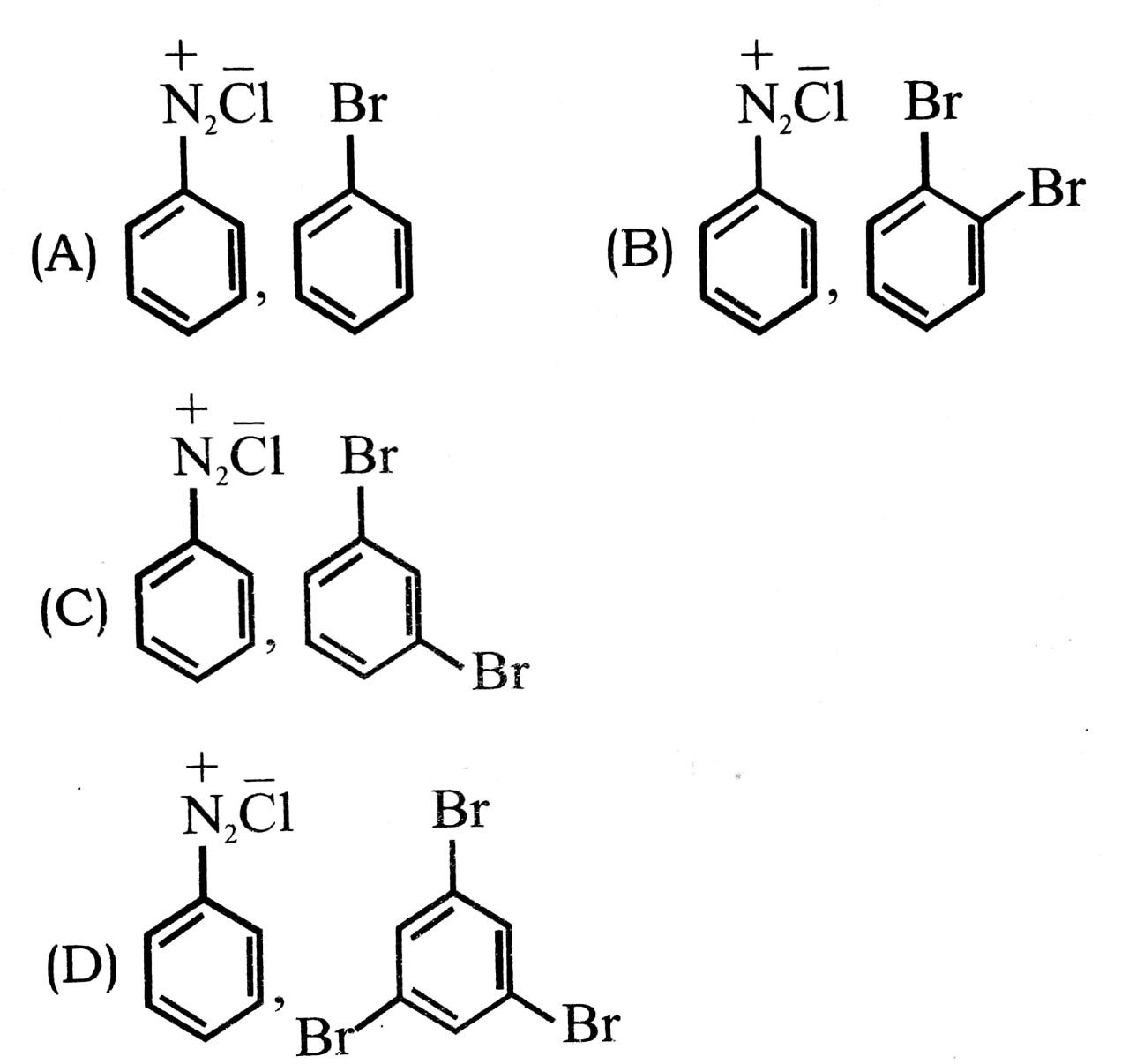
17. Which one of the following is not correct order of boiling points of the alkyl/aryl halides ?
(A) CHCl3 > CH2Cl2
(B) CH3(CH2)3Cl > CH3(CH2)2Cl
(C) (CH3)3CCl > (CH3)2 CHCH2Cl
(D) CH3(CH2)3Cl > CH3CH CHClCH3
18. Which of the following compounds will have highest melting point ?
(A) Chlorobenzene
(B) o-Dichlorobenzene
(C) m-Dichlorobenzene
(D) p-Dichlorobenzene
19. Ethyl alcohol is obtained when ethyl chloride is boiled with
(A) alcoholic KOH
(B) aqueous KOH
(C) water
(D) aqueous KMnO4
20. Which of the following alkyl halides undergoes hydrolysis with aqueous KOH at the fastest rate ?
(A) CH3CH2CH2Cl
(B) CH3CH2Cl
(C) CH3CH2CH2CH2Cl
(D) CH3CH2CH (Br) CH3
21. The alkyl halide is converted into an alcohol by
(A) elimination
(B) dehydrohalogenation
(C) addition
(D) substitution
22. A mixture of 1-chloropropane and 2- chloropropane when treated with alcoholic KOH gives
(A) prop-1-ene
(B) prop-2-ene
(C) a mixture of prop-1-ene and prop-2-ene
(D) propanol
23. Arrange the following alkyl halides in order of dehydrohalogenation
C2H5I, C2H5 Cl, C2H5Br, C2H5F
(A) C2H5H > C2H2Cl > C2H5Br > C2H2I
(B) C2H5I > C2H5Br > C2H5Cl > C2H5F
(C) C2H5I > C2H5Cl > C2H5Br > C2H5F
(D) C2H5F > C2H5I > C2H5Br > C2H5Cl
24. Tertiary alkyi halides are practically inert to substitution by S N2 mechanism because
(A) the carbocation formed is unstable
(B) there is steric hindrance
(C) there is inductive effect
(D) the rate of reaction is faster in S N2 mechanism
25. The order of reactivity of following alcohols with halogen acids is
I. CH3CH2 – CH2 – OH II. CH3CH2 CH – OH
. ![]()
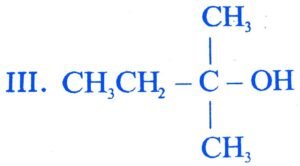
(A) I > II > III
(B) III > II > I
(C) II > I > III
(D) I > III > II
26. Identify the compound ‘Y’ in the following reaction :


27. Arrange the following compounds in the increasing order of their densities
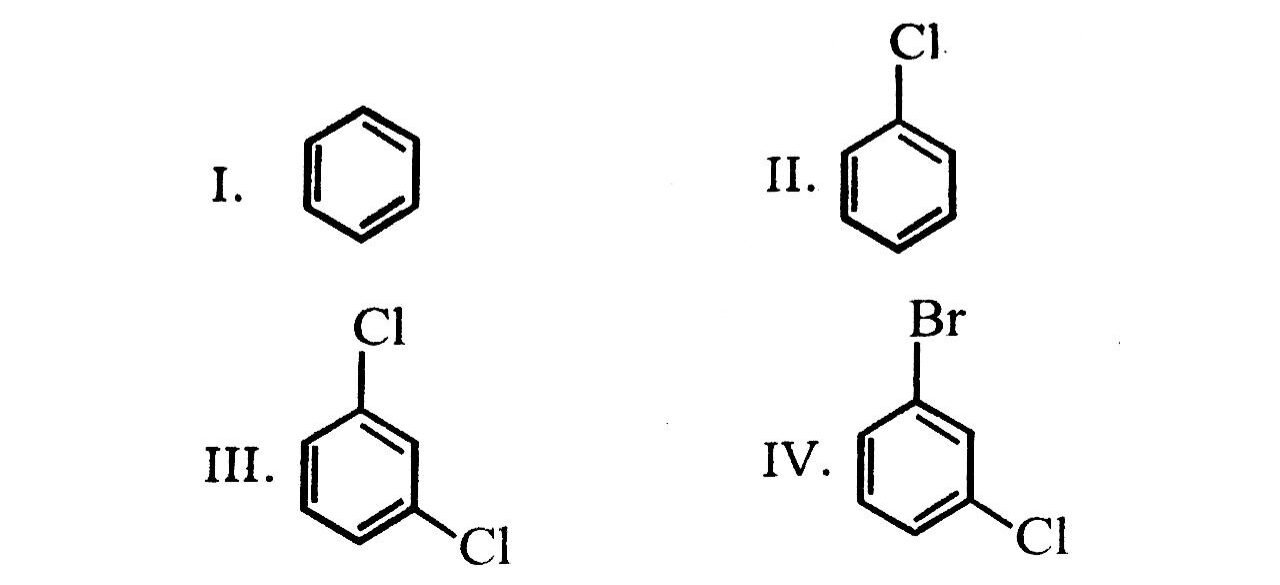
(A) I < II < III < IV
(B) I < III < IV < II
(C) IV < III < II < I
(D) II < IV < III < I
28. Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their boiling point
I. ![]() CH – CH2Br II. CH3CH2CH2CH2Br
CH – CH2Br II. CH3CH2CH2CH2Br
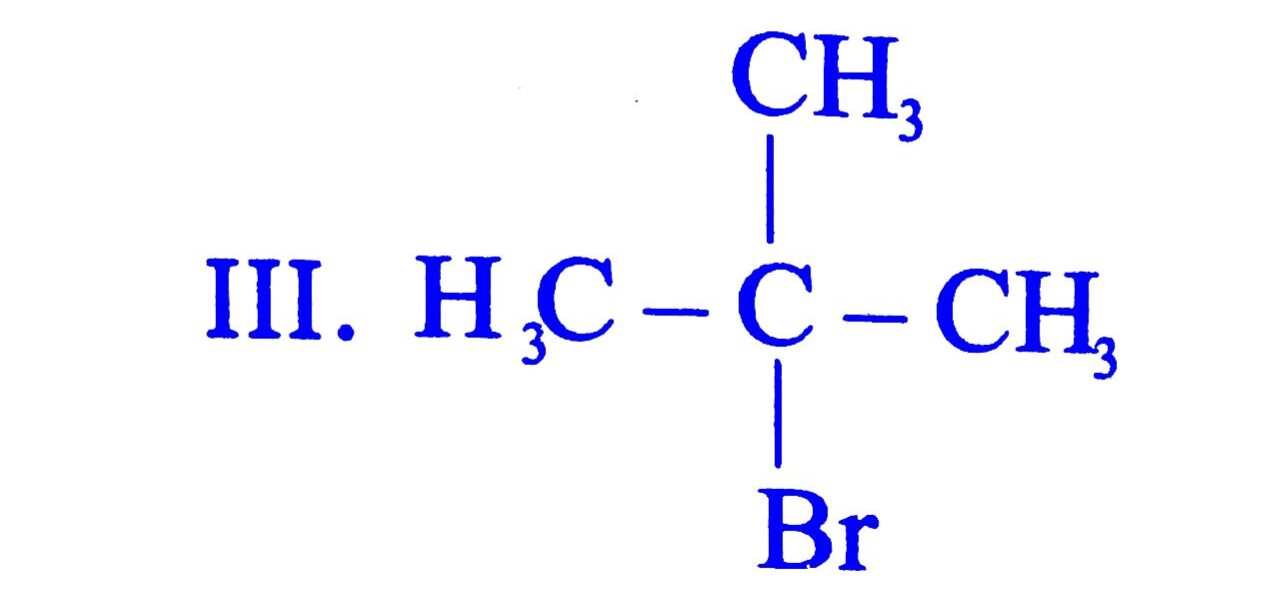
(A) II < I < III
(B) I < II < III
(C) III < I < II
(D) III < II <I
29. A primary alkyl halide would prefer to undergo
(A) SN1 reaction
(B) SN2 reaction
(C) α-elimination
(D) racemisation
30. Reaction of C6H5CH2Br with aqueous sodium hydroxide follows
(A) SN1 mechanism
(B) SN2 mechanism
(C) Any of the above two depending upon the temperature of reaction
(D) Saytzeff rule
31. Which of the following compounds will give racemic mixture on nucleophilic substitution by OH-ion ?
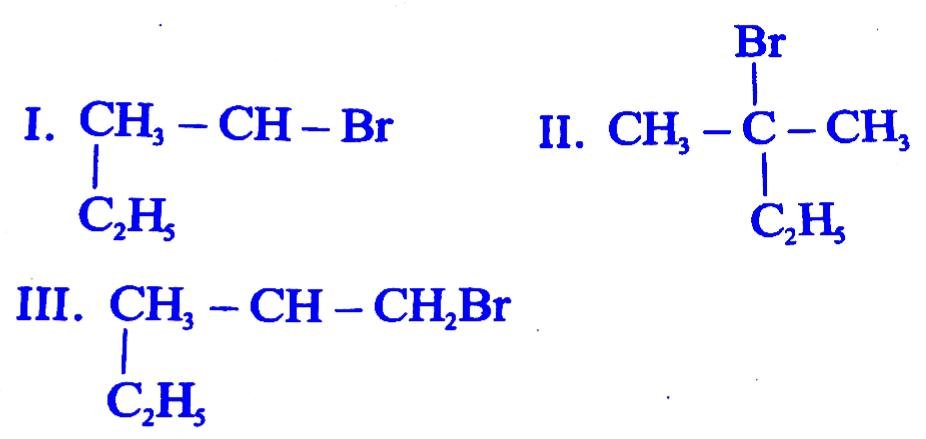
(A) I
(B) I, II, III
(C) II, III
(D) I, III
32. A Grignard reagent is prepared by the action of magnesium in dry ether on ?
(A) C2H5OH
(B) C2H6
(C) C2H5Cl
(D) C2H5CN
33. Primary, Secondary and Tertiary alcohols are distinguished by
(A) Oxidation method
(B) Lucas reagent method
(C) Victor Meyer’s method
(D) All of these
34. Ethyl acetate reacts with CH2MgBr to from
(A) Secondary alcohol
(B) Tertiary alcohol
(C) Primary alcohol and Acid
(D) Carboxylic acid




